About This Article
Zoom Health has supplied hearing protection equipment to UK customers for nearly 20 years. This guide draws on our experience helping thousands of people select the right ear protection for workplace safety, shooting sports, and noise-sensitive environments. Always follow workplace safety regulations and consult guidance from the UK Health & Safety Executive for hearing protection requirements.
Published: April 2019 | Last Updated: November 2025 | By: Anthony Cunningham
Contents
What Are Corded Earplugs?
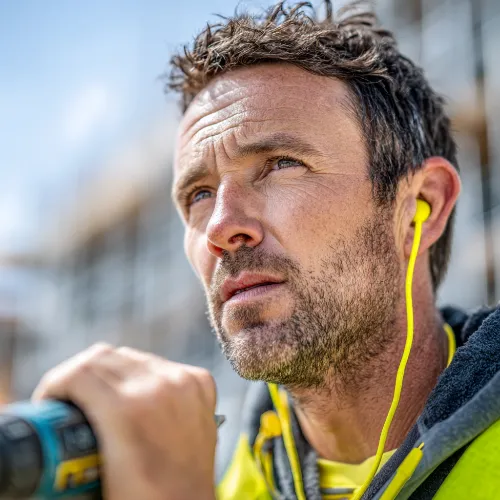
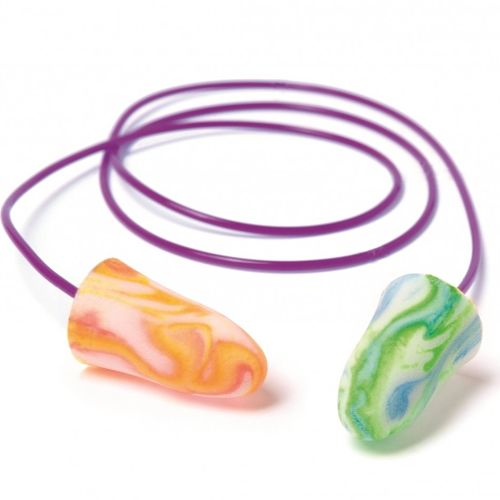
When you have a pair of regular earplugs that have a cord attached to each end we call these corded earplugs. These are usually made with plastic or vinyl. This allows the user to quickly insert or remove their earplugs whenever they want to. You can easily hang your earplugs around your neck and quickly put them in again or take them out whenever you deem necessary.
In an area such as a factory or where there are noisy machines present, earplugs that have a cord are often used. An employee might be moving from a noisy area into a quiet area frequently so they can simply take them out and put them in again when required. These plugs are also easy to retrieve or detect if you happen to drop them or lose them due to the presence of the cord.
Mini corded earplugs are made with foam as this is a common type. The cord itself will usually be made out of flexible plastic. These plugs are durable and quite inexpensive. Employers often give these to their employees so that their hearing is protected during working hours.
A corded earplug is also popular with those that go to a firing range or enjoy hobbies like clay pigeon shooting as it helps to protect the ears from gunfire noise. These plugs are inserted into the ears before a firearm is discharged and then they can be taken out once the shooter has finished. It is critical that you protect your ears from high decibel noise like gunshots. These types of earplugs can also make it difficult for you to hear general communication or conversations so you need earplugs that are easily removed and then put back again when you need hearing protection again.
Another major benefit of using an earplug that is corded rather than an individual plug is that you won’t lose them if one earplug happens to fall out because they have a cord attached. The other one is usually going to remain in place. A single plug that falls out of your ear can be harder to locate since there is no cord attached.
Why Choose Corded Earplugs
A corded earplug can be a better solution to one that doesn’t have a cord because they are easier to work with and manage. You won’t have to worry as much about losing your ear plug since both plugs are attached with a cord. In compliance with HSE hearing protection standards for workplace noise exposure, corded earplugs are a practical choice for employers seeking to protect their workforce whilst maintaining operational flexibility.
Best Corded Earplugs
We’ve selected six of the highest-rated corded earplugs available on the market today. All meet UK workplace safety standards and offer reliable hearing protection across a range of environments:
Laser Lite Corded Soft Foam Earplugs
From £2.99
Uvex com4-fit – Corded Earplugs
From £0.99
Mack’s Acoustic Foam Corded Earplugs
£4.99 (reduced from £6.99)
What Customers Say
★★★★★ Ruby – April 2025
“Absolutely love these! I’ve ordered the 50 pack at least 3 times now. They’re so comfortable and block out the perfect amount of noise to sleep with. The delivery is also super quick.”
★★★★★ C M Roberts – April 2025
“Great product, great price, speedy delivery! Exactly what I needed for workplace hearing protection.”
Materials & Comfort Considerations
When selecting corded earplugs, the material composition directly affects comfort during extended use and long-term durability. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right option for your needs.
Material Types
- Foam (PU/Melamine): Soft and compressible, foam earplugs mould to the ear canal for a secure fit. They’re comfortable for most users but degrade over time and are typically single-use or short-term. Excellent noise reduction (28–32 dB).
- Silicone: Pre-moulded silicone earplugs are durable, washable, and reusable for months or years. Slightly firmer than foam, but better value over time and less environmental waste.
- Elastomer/Thermoplastic: A hybrid material combining properties of both foam and silicone. Durable, comfortable, and often available in multiple sizes for better fit customisation.
For full-time workers in loud environments, silicone or elastomer options offer better cost-effectiveness despite higher upfront costs, as they last much longer than foam. For occasional use—such as shooting sports or periodic factory work—foam earplugs offer superior comfort and cost savings.
Decibel Ratings & Workplace Standards
The Noise Reduction Rating (NRR) indicates how many decibels of sound an earplug will reduce. However, real-world protection is typically 25–50% lower than the stated NRR, so a 30 dB earplug might provide 15–22 dB of actual protection depending on fit and insertion technique.
According to HSE guidance on workplace noise exposure, employers must provide hearing protection when employees are exposed to noise levels exceeding 80 dB over an 8-hour day. At 85 dB or higher, hearing protection becomes mandatory. Most corded earplugs with an NRR of 28–32 dB are suitable for factory, construction, and shooting environments where noise levels regularly exceed 100 dB.
Common Use Cases
Corded earplugs are versatile hearing protection suited to several environments and activities:
- Factory & Manufacturing: Workers frequently move between loud machinery areas and quieter zones. Corded earplugs can be inserted when entering noisy sections and removed when returning to quieter areas, without risk of loss.
- Construction Sites: From power tool use to heavy machinery operation, construction environments often require intermittent hearing protection.
- Shooting Ranges & Clay Pigeon Shooting: Shooters benefit from quick insertion before discharge and removal during quiet moments, whilst complying with shooting safety protocols.
- Maintenance & Mechanical Work: Vehicle mechanics, HVAC technicians, and equipment repair workers use corded earplugs to protect against pneumatic tools, compressors, and impact noise.
- Live Event & Concert Venues: Security staff and crew members use corded earplugs whilst protecting against sustained high-decibel sound.
Tips for Durability & Comfort
Maximising comfort and lifespan requires proper use and care of your corded earplugs.
✓ Insertion Technique: Roll foam earplugs between your fingers to compress them, then insert slowly into the ear canal. Allow the foam to expand naturally for a tight seal. Incorrect insertion can reduce noise reduction effectiveness by 50% or more.
✓ Clean & Store Properly: If using reusable silicone earplugs, wash them regularly with warm soapy water and allow them to air dry. Store in a clean, dry container away from direct sunlight.
✓ Replace Foam Earplugs Regularly: Disposable foam earplugs lose their acoustic properties after 1–2 weeks of regular use. Replace them if you notice reduced comfort or noise reduction.
✓ Check the Cord: Inspect the connecting cord periodically for cracks, fraying, or damage. A damaged cord reduces the protective benefit.
✓ Workplace Fit Testing: Many UK employers offer workplace fit testing to ensure employees are using hearing protection correctly. Ask your line manager about fit testing if your workplace hasn’t provided it.
Ready to find the perfect corded earplugs for your needs? Browse our complete selection—from budget-friendly options to premium hearing protection. All products include next-day delivery and come backed by our 20-year expertise.
About the Author
Anthony Cunningham – Health Writer & Editor
Anthony Cunningham, BA (Hons), MA, is a UK-based health writer and editor with over 20 years’ experience running Zoom Health, a trusted source for home health tests, preventive care, workplace safety products, and wellness guidance. He creates clear, evidence-based articles using NHS, NICE, HSE, and WHO guidance. Where possible, content is reviewed by practising clinicians and safety professionals to enhance accuracy and reliability, helping readers and workplace managers make informed decisions about hearing protection and occupational health.
You May Also Like
Explore more articles on hearing protection and workplace safety: